Supply Chain Guide
What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management is the process of delivering a product from raw materials to the consumer. It includes supply planning, product planning, demand planning, sales, and other operations of planning and supply management.
Why Supply Chain Management is Important
The positive or negative impact on the supply chain is felt throughout the business. There are two main areas of impact: customer satisfaction and return on investment.
A satisfied customer is equal to a profitable business and also means higher productivity.
If a customer is happy with the way the return was handled, they are 70 percent more likely to be a repeat customer.
A smooth return process means an efficient supply chain that is well-connected and involves interaction throughout the entire supply chain. When the supply chain meets or exceeds customer expectations, it is due to efficiency. The entire business benefits from higher rates, positive customer sentiment, and lower service costs for the business.
Higher Productivity in The Supply Chain
Higher productivity is measured in terms of the efficiency of all processes of delivering goods and services along the supply chain.
Improving supply chain efficiency can put pressure on the team and its capabilities, as costs and budgets remain flat or cut when they are expected to move the same or more products at the same or higher quality levels.
The increase in profit for the business is measured using indicators such as working capital turnover or cash conversion. As the business improves, the result is profitable cash management and income transformation. Flattening the cost curve is often a challenge if two factors are not considered: new capabilities (process and data) that enable faster, better decision-making; and the use of a tool that scales profitably based on the value it brings to the business.
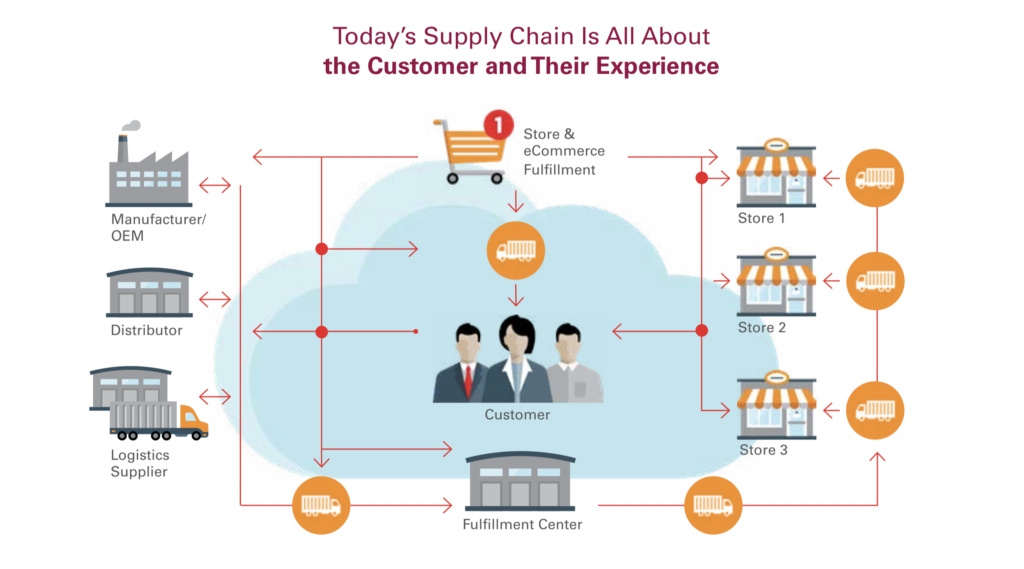
What is the Supply Chain Management Process?
The supply chain management process consists of four main parts: demand management, supply chain management, S&OP, and product portfolio management.
1. Demand management
Demand management has three parts: demand planning, product planning, and trade promotion planning.
Demand planning is the process of forecasting demand to ensure reliable delivery of products. Effective demand planning can clear the accuracy of revenue forecasts, align inventory levels with demand peaks and troughs, and increase profitability for a particular channel or product.
Item scheduling is a systematic approach to planning, buying and selling items with the goal of maximizing your return on investment (ROI) while making items available at the locations, times, prices and quantities required by the market.
Promotional planning is a marketing method for increasing the demand for products in retail stores based on special prices, display fixtures, demonstrations, value-added bonuses, gifts, and other promotions. Promotions help stimulate short-term consumer demand for products typically sold in retail.
2. Supply management
Supply management is generally divided into supply planning, production planning, inventory planning, capacity planning, and distribution planning.
Supply planning determines how best to meet the requirements generated from the sales plan. The goal is to balance supply and demand in such a way as to achieve the financial and service objectives of the enterprise.
Production planning refers to production and production modules within a company. It takes into account the allocation of employee resources, materials and production capacity.
Production Planning
Inventory scheduling determines the optimal quantity and timing of inventory to align with sales and manufacturing needs.
Capacity planning identifies the production personnel and equipment needed to meet product demand.
Distribution planning and network planning control the movement of goods from a supplier or manufacturer to the point of sale. Distribution management is a catch-all term that refers to processes such as packaging, inventory, warehousing, supply chain, and logistics.
Sales and Operations Planning
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) is a periodically integrated management process that allows focusing on key supply chain factors like sales, marketing, demand management, manufacturing, inventory management, and new product features.
With a focus on financial and business impact, S&OP’s goal is to empower leaders to make better decisions by dynamically linking plans and strategies across the business. The S&OP, which is repeated frequently on a monthly basis, enables efficient supply chain management and focuses the organization’s resources on delivering what their customers need while remaining profitable.
Product and General Portfolio Management
Product portfolio management is the process of creating a product idea to bring to the market. A company must have an exit strategy for its product when it reaches the end of its profitable life or if the product does not sell well.
Product Portfolio Management Includes:
- New product introduction
- End-of-life planning
- Cannibalization planning
- Commercialization and ramp planning
- Contribution margin analysis
- Portfolio management
- Brand, portfolio and platform planning
Best Practices in Supply Chain Management.
To succeed in a growing global marketplace, you need a connected end-to-end supply chain inside and outside your enterprise.
When using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and spreadsheets for planning, companies typically rely only on historical data, which leaves little room for change in the event of any disruption in supply or demand. For example, based on the previous year’s performance, a company can estimate the number of products it will sell in the next quarter. But what if a major hurricane destroys a key distribution centre, resulting in too little inventory on the shelves? With a mindful, real-time, supply chain planning solution, you can create “what-if” scenarios and plan more efficiently.